Order to Cash (O2C) Cycle
Order to Cash means Customer’s Order Placing to Vendor’s Cash Receiving. When your final product is ready to be sold, you market it. The customer gets fascinated with the marketing campaign and decides to buy your product and from here starts the O2C cycle.Step 1] Order Entry:
Customer sends details of order or sales dept brings order from customers. After that the order is entered in Order Management (OM)
Navigation: Order Management Super User> Orders Returns >Sales Orders
Here we need to enter the Customer Details (Customer Name , Number, Contact Ship to and Bill to address etc.), Order type. In the Lines tab we need to enter the Item to be ordered and the quantity required. Here we can also check the availability of the order. Here we can save the order. Once saved the Order Status is changed to ‘Entered’.
Key Tables:
- OE_ORDER_HEADERS_ALL – All header information is stored here.
- OE_ORDER_LINES_ALL – All the line information is stored here.
When we book the order, we are just confirming and freezing our order.
The final step in the Sales Order Entry process is to Book the order. This signifies that the Order Entry process is complete and that the order is eligible for the next stage in the line flow for this order, as defined by its Transaction Type. Select the Book Order button. The Entry Status of the Order will change to Booked.
After Order Booking:
Order Header: Booked
Order Line : Awaiting Shipping
Shipping Transaction form: Ready to release
Table Level :
- OE_ORDER_HEADERS_ALL : Flow_Status_code –Booked
- OE_ORDER_LINES_ALL : Flow_Status_code – Awaiting Shipping
- WSH_DELIVERY_DETAILS : Released_Status – R ( means – Ready to release)
Pick Release is the process in which the items on the sales order are taken out from inventory.
Navigation: Order Management Super User> Shipping > Release sales Orders > Release sales order
Based On rule: Select the Grouping rule the reaming details will default in Order, Shipping and Inventory tab
Order Tab:
- Order Number: Select the Order Number. Values for the Order Type and Customer fields of this form default to those for the order number you enter here.
- Ship Set: Select the Ship Set to be released. The Order Number must be selected first.
- Auto creates Deliveries : Select Yes in this box to automatically create deliveries for delivery lines once they are released
- Release Sequence Rule: Select Rule to specify the order in which the picking lines are released.
- Auto Pick Confirm –Yes/No
- Warehouse: Select the Warehouse
- Sub inventory: Select the Sub inventory
- Pick Slip Grouping Rule: To determine how released picking lines are grouped onto pick slips.
- Default Stage Sub inventory: Select the Default Stage Sub inventory
- OE_ORDER_LINES_ALL (flow_status_code ‘PICKED’ )
- WSH_DELIVERY_DETAILS (released_status ‘S’ ‘submitted for release’ )
- mtl_txn_request_headers
- mtl_txn_request_lines
- Mtl_material_transactions_temp (link to above tables through move_order_header_id/line_id
If Auto Pick Confirm in the above step is set to NO, then the following should be done.
Navigation: Inventory Super User > Move Order> Transact Move Order
In the HEADER tab, enter the BATCH NUMBER (from the above step) of the order. Click FIND. Click on VIEW/UPDATE Allocation, then Click TRANSACT button. Then Transact button will be deactivated then just close it and go to next step.
- Items are transferred from salable to staging Sub inventory.
- mtl_material_transactions
- mtl_transaction_accounts
- wsh_delivery_details (released_status ‘Y’ ‘Released’ )
- wsh_delivery_assignments
The Shipping Transaction window provides a centralized workbench that consolidates three major shipping functions: planning, pick releasing, and ship confirming.
Navigation: Order Management Super User>Shipping >Transactions.
Here ship confirm interface program runs in background . Data are removed from wsh_new_deliveries.
- oe_order_lines_all (flow_status_code ‘shipped’)
- wsh_delivery_details (released_status ‘C’ ‘Shipped’)
- mtl_transaction_interface
- mtl_material_transactions(linked through Transaction source header id)
- mtl_transaction_accounts
Step 6] Enter Invoices in Receivables:
Run workflow background Process. Workflow Background Process inserts the records in RA_INTERFACE_LINES_ALL with
- INTERFACE_LINE_CONTEXT = ’ORDER ENTRY’
- INTERFACE_LINE_ATTRIBUTE1 = Order_number
- INTERFACE_LINE_ATTRIBUTE3 = Delivery_id
Navigation: Order Management >view >Requests
Underlying tables:
- RA_CUSTOMER_TRX_ALL will have the Invoice header information. The column INTERFACE_HEADER_ATTRIBUTE1 will have the Order Number.
- RA_CUSTOMER_TRX_LINES_ALL will have the Invoice lines information. The column INTERFACE_LINE_ATTRIBUTE1 will have the Order Number.
In this stage order line level table get updated with Flow status and open flag .
- oe_order_lines_all (flow_status_code ‘shipped’, open_flag “N”)
This is last step of Order Processing . In this stage only oe_order_lines_all table get updated .
- oe_order_lines_all (flow_status_code ‘closed’, open_flag “N”)
What’s New in R12 Financials?
What’s New in R12 Financials?
1] Ledgers and Ledger Sets:The ledger is a new fundamental concept in Release 12. The ledger replaces the 11i concept of a set of books. It represents an accounting representation for one or more legal entities or for a business need such as consolidation or management reporting.
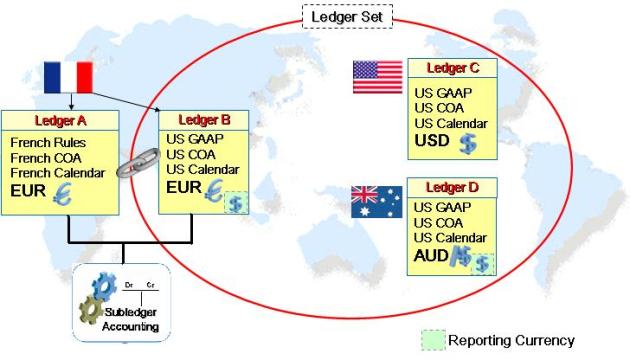
11i & Prior = Sets of Books (3 C’s)
- Chart of Accounts
- Accounting Calendar
- Currency
- Chart of accounts
- Ledger currency
- Accounting calendar
- Accounting method – new 4th
Primary Ledger:
- The main “Activity” Ledger
- Usually in the local currency
- For Operational reporting
- Differs from Primary Ledger by Chart of Account, Calendar, and/or Accounting Method
- For Statutory, Tax or Consolidated reporting
- Differs from Primary Ledger by Currency ONLY
- Just a translation of the Primary Ledger – no rules required
- For Consolidated reporting
- Grouping of ledgers with the same chart of accounts and calendar/period type combination
- Essentially treats multiple ledgers as one

You can consider SLA as a bridge or an Intermediate platform that talks to Subledger products (these are other applications or modules) and the General ledger. All Accounting entries for your modules (like AP, AR, Projects, Inventory, etc) are treated as Sub-Ledgers and they first sent to the SLA engine. The SLA applies its rules (some or these rules are pre-configured and also you can configure as many rules as you want) and then sends the necessary journal entries to the General ledger.
In a nutshell, the following services are provided by Oracle SLA
- Rule based Generation and storing of accounting entries
- Storing subledger balances
- Subledger or SLA accounting entries
- Subledger reporting (some examples could be Open Account Balances Listing and Subledger Journal Reports, etc )
‘Multi-Org Access Control’ popularly known as ‘MOAC’ in short form is an enhanced feature in Release 12. MOAC will enable users to access secured data in one or more Operating Units from a single responsibility.

End-Users can access/transact data within several operating units based on Security Profile attached to a responsibility. i.e. End-Users can access/transact data on multiple Operating units by accessing one operating unit at a time without changing a responsibility. This Provides flexibility for end-users to work conveniently with multiple Operating Units in shared service Environments with single responsibility.
4] Advanced Global Intercompany System (AGIS):

Advanced Global Intercompany System (AGIS) enables you to create, settle and reconcile intercompany transactions. Intercompany transactions are transactions that occur between two related legal entities in an enterprise or between groups in the same legal entity. The balances of the intercompany transactions must be eliminated or adjusted when preparing the consolidated financial statement, or it might result in overstated financial results, which in turn might lead to legal repercussions against the enterprise. Intercompany transactions can be identified and eliminated by the use of specific accounts to book these transactions.
5] Tax Engine:
It Centrally manage tax transactions across entire E-Business Suite.
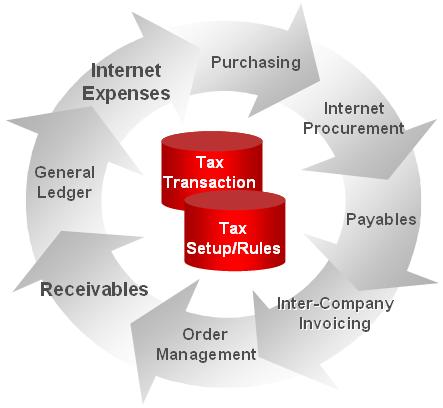
- Single Repository of transactions for global business insight
- Centralized rules applied to transactions to manage globally and reduce risk
- Automation of tax processes on transactions to improve operational efficiency
- Improved Reporting
- Effective Date Setup
- Extensible architecture that supports additions, e.g. Self-assessed Use Tax
Because of changing business need and high demand of global partners, the R12 release witness great changes ever into the bank model. Bank account is now associated with Legal entity rather than Operating Unit and hence single bank account serves multiple Operating Units. This makes bank with strong capability to pay across operating units. More over banks accounts can be shared by applications and can be designed for use by Payables, Receivables and Payroll.
The new bank account model allow you to define and keep track of all bank accounts in the e-Business Suite in one place and explicitly grant account access to multiple operating units/functions and users. The new model reduces the number of access points to manage bank accounts by providing a centralized user interface where all internal bank accounts can be set up.
No comments:
Post a Comment